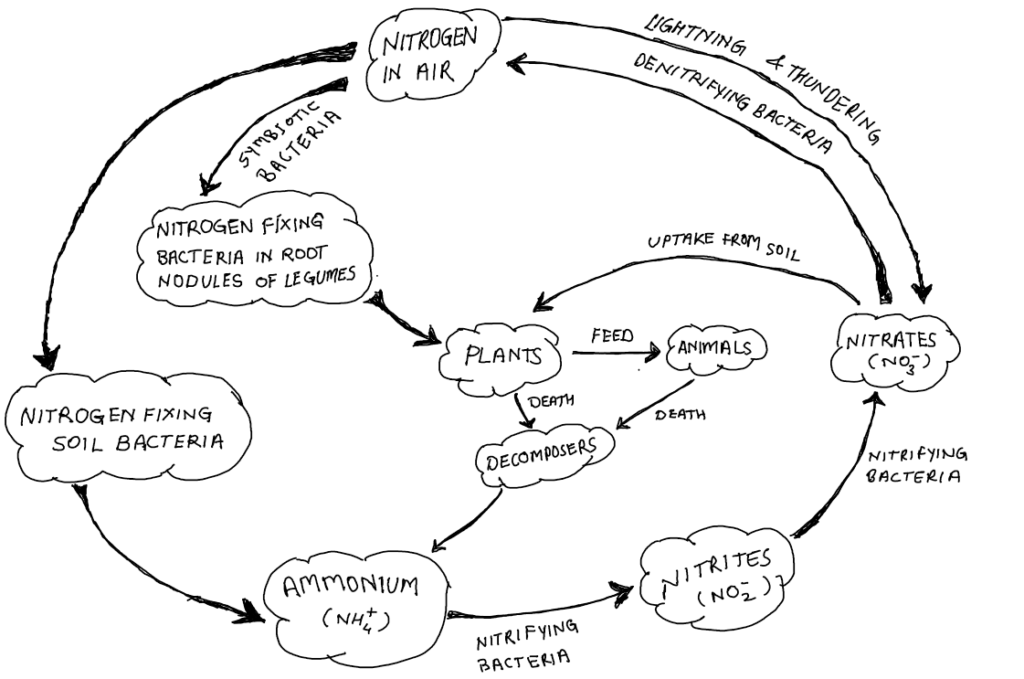
Nitrogen fixation is a process by which atmospheric nitrogen (which is not usable form for the organisms) get converted into its compounds (ammonia, nitrates and nitrites) which can be used easily by organisms.
Nitrogen is an important constituent element of the proteins and the nucleic acids. All organisms required nitrogen but only plant can take nitrogenous compound from the soil. Animals depend directly or indirectly on the plants for their nitrogen requirement.
In the air, by volume 78% nitrogen is present. But plants cannot use this directly from the air. They uptake it as compound from the soil.
Nitrogen fixation may take place biologically or non-biologically. Biological Nitrogen fixation is carried out naturally in soil by micro-organisms. Some symbiotic (Rhizobium) and free-living (Cyanobacteria) bacteria have ability to convert atmospheric molecular nitrogen into its compounds. Whereas, sometimes nitrogen gets fixed through the action of lightning which is non-biological nitrogen fixation.
Nitrogen cycle:
Nitrogen cycle is a series of processes that convert nitrogen gas to organic substances and back to nitrogen in nature.
- Fixation of atmospheric molecular nitrogen by certain bacteria (biological fixation) and by lightening (non-biological fixation).
- Up taking of nitrogenous compound by plants through their roots. Nitrogen is then used for the synthesis of plant proteins and other compounds.
- Animals feeding on plants get these proteins and other nitrogenous compounds.
- Animal excreta, dead animals and plant parts are decomposed by bacteria and fungi present in the soil producing simple nitrogenous compounds to be used by plants again.
- Certain other bacteria convert some part of nitrogenous compound to nitrogen gas which goes back into the atmosphere. As a result, the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere remains more or less constant.