In the living world, there are various kind of organism. Some organisms are huge sized like elephant and whale, some are small in size as ant and other small insects. But there are extremely small organisms also found which we normally cannot see. These extremely small organisms are called microorganisms or microbes. These are so small in size that they cannot be seen with the unaided eye. We need microscope to see microbes. Water and soil are full of microorganisms. Microorganisms are useful (used to prepare manure) as well as harmful (disease causing microbes).
Classification of microorganism:
Microorganisms are classified into four major groups.
Viruses are also microscopic but are different from other microorganisms.
Virus:
- Viruses are microscopic organization of proteins and nucleic acids which exhibit living like characters only inside the host cells.
- Virus behaves as non-living when it is outside the host cell. Therefore, we can say that viruses are connecting link between livings and non-livings.
- Viruses may reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism, which may be a bacterium, plant or animal.
- Viruses are responsible for many diseases like; common cold, flu, AIDS, dengue, covid-19 etc.
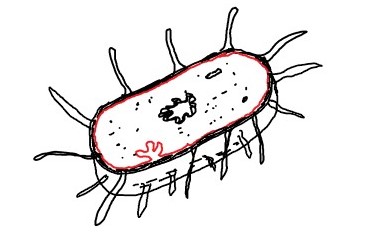
Bacteria:
- Bacteria are unicellular, prokaryotic organisms. Singular of bacteria is bacterium.
- Bacteria are cosmopolitan, means they live in all types of environments, ranging from ice cold climate to hot springs; and deserts to marshy lands. They also found inside the bodies of animals including humans.
- Bacteria found in different shapes; like rod-shaped, spiral, spherical and comma-shaped.
- Some of them are autotrophic (prepare their own food), while others are heterotrophic (depend on others for their food).
Fungi:
- Fungi are eukaryotic, mainly multicellular organisms (except yeast).
- These are saprotrophic (obtain food from dead and decaying matter).
- Some fungi are parasites of plants and animals causing diseases (such as mildews, rusts, scabs or canker in plants and skin diseases in human).
- Few fungi live in symbiotic association with other organisms like lichen, mycorrhiza.
- Warm and moist conditions are suitable for the growth of fungi.

Algae:
- Alga is a green plants. Its body is not differentiate into root, stem and leaves.
- These are autotrophic. All algae contain chlorophyll and can synthesize food their own by the process of photosynthesis.
- They prefer mostly aquatic habitats.
- Some common examples of alae are: Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Chlamydomonas.
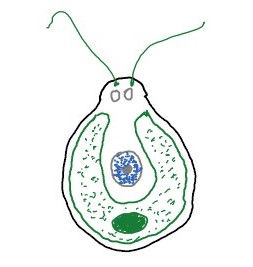
Protozoa:
- protozoans are single cell, eukaryotic organisms.
- These organisms found in different shapes and sizes ranging from an Amoeba which can change its shape to Paramecium with its fixed shape and complex structure.
- Protozoans prefer moist & aquatic habitats.
- Diseases like dysentery and malaria are caused by protozoa.
